import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sympy import Max
from epymorph.kit import *
from epymorph.adrio import acs5Seasonality Beta Editing
SCENARIO:
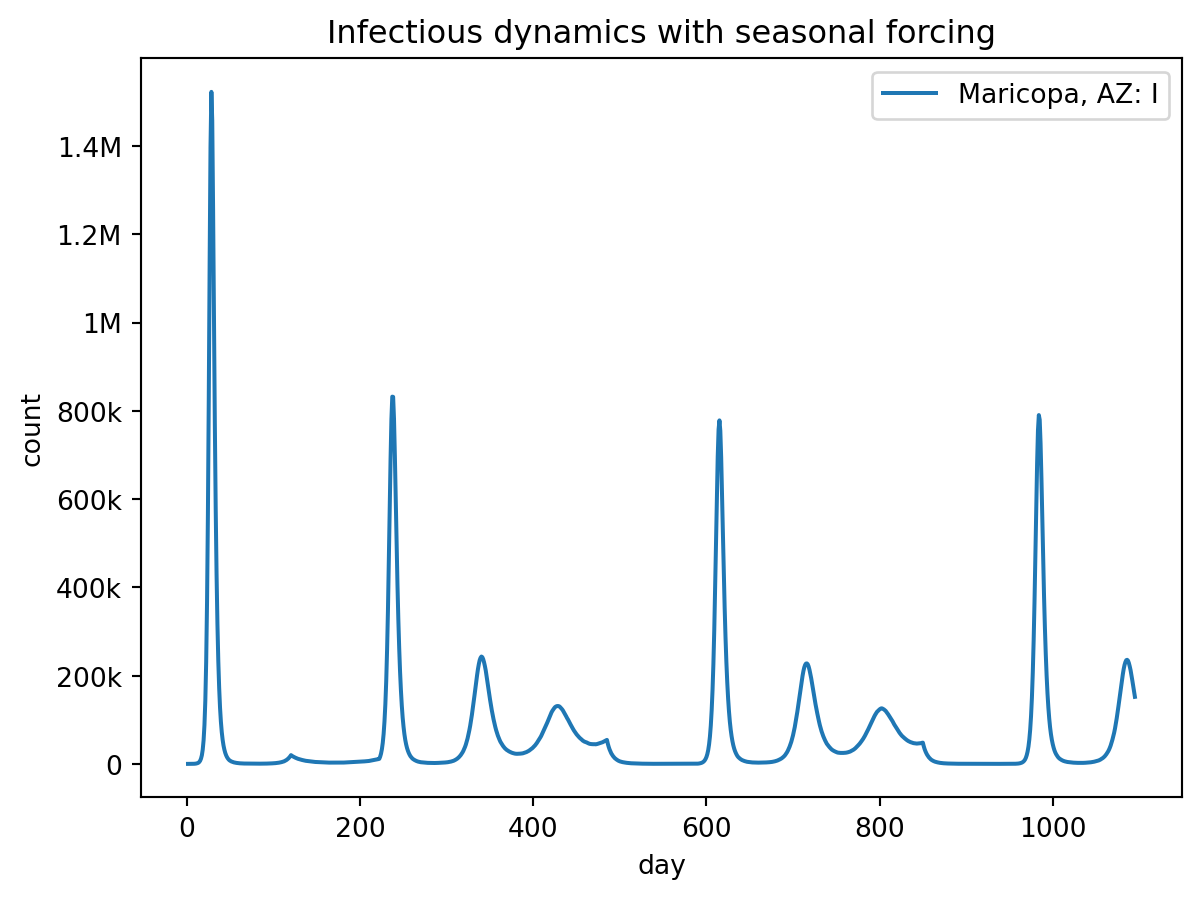
In many modeling scenarios, it is important to account for seasonal changes in the transmission rate of a pathogen. A classic example is measles, which typically circulates amongst school-aged children. Transmission rate is assumed to be higher during the academic year, but lower in the summer months, when there is less indoor contact between school-aged children. We can address this issue by assuming a time-varying rate of transmission in the model. The exercises in this vignette show you how to do this in epymorph, as well as exploring how seasonally-changing transmission rates can lead to stable cycling of a disease.
Exercise
class SIRS(CompartmentModel):
"""Defines a compartmental IPM for a generic SIR model."""
compartments = [
compartment('S'),
compartment('I'),
compartment('R'),
]
requirements = [
AttributeDef('beta', type=float, shape=Shapes.TxN,
comment='infectivity'),
AttributeDef('gamma', type=float, shape=Shapes.TxN,
comment='recovery rate'),
AttributeDef('latent', type=float, shape=Shapes.TxN,
comment='recovery rate'),
]
def edges(self, symbols):
[S, I, R] = symbols.all_compartments
[β, γ, l] = symbols.all_requirements
N = Max(1, S + I + R)
return [
edge(S, I, rate=β * S * I / N),
edge(I, R, rate=γ * I),
edge(R, S, rate=l * R),
]class Step_Beta(ParamFunctionTimeAndNode):
def evaluate1(self, day: int, node_index: int) -> float:
winter_beta = 1.0
summer_beta = 0.5
summer_start = 120
summer_end = 221
t_mod = day % 365
if summer_start <= t_mod <= summer_end:
x = summer_beta
else:
x = winter_beta
return xscope = CountyScope.in_counties(['Maricopa, AZ'], year=2020)
my_ipm = SIRS()
null_mm = mm.No()
rume = SingleStrataRUME.build(
ipm=my_ipm,
mm=null_mm,
init=init.SingleLocation(location=0, seed_size=5),
scope=scope,
time_frame=TimeFrame.of("2015-01-01", 365 * 3),
params={
'beta': Step_Beta(),
'gamma': 1 / 3,
'latent': 1 / 120,
'population': acs5.Population(),
}
)# Evaluate the transmission rates
beta_values = (
Step_Beta()
.with_context(
scope=rume.scope,
time_frame=rume.time_frame,
)
.evaluate()
)
### GRAPH ###
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(beta_values)
ax.set(title="beta function", ylabel="beta", xlabel="days")
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()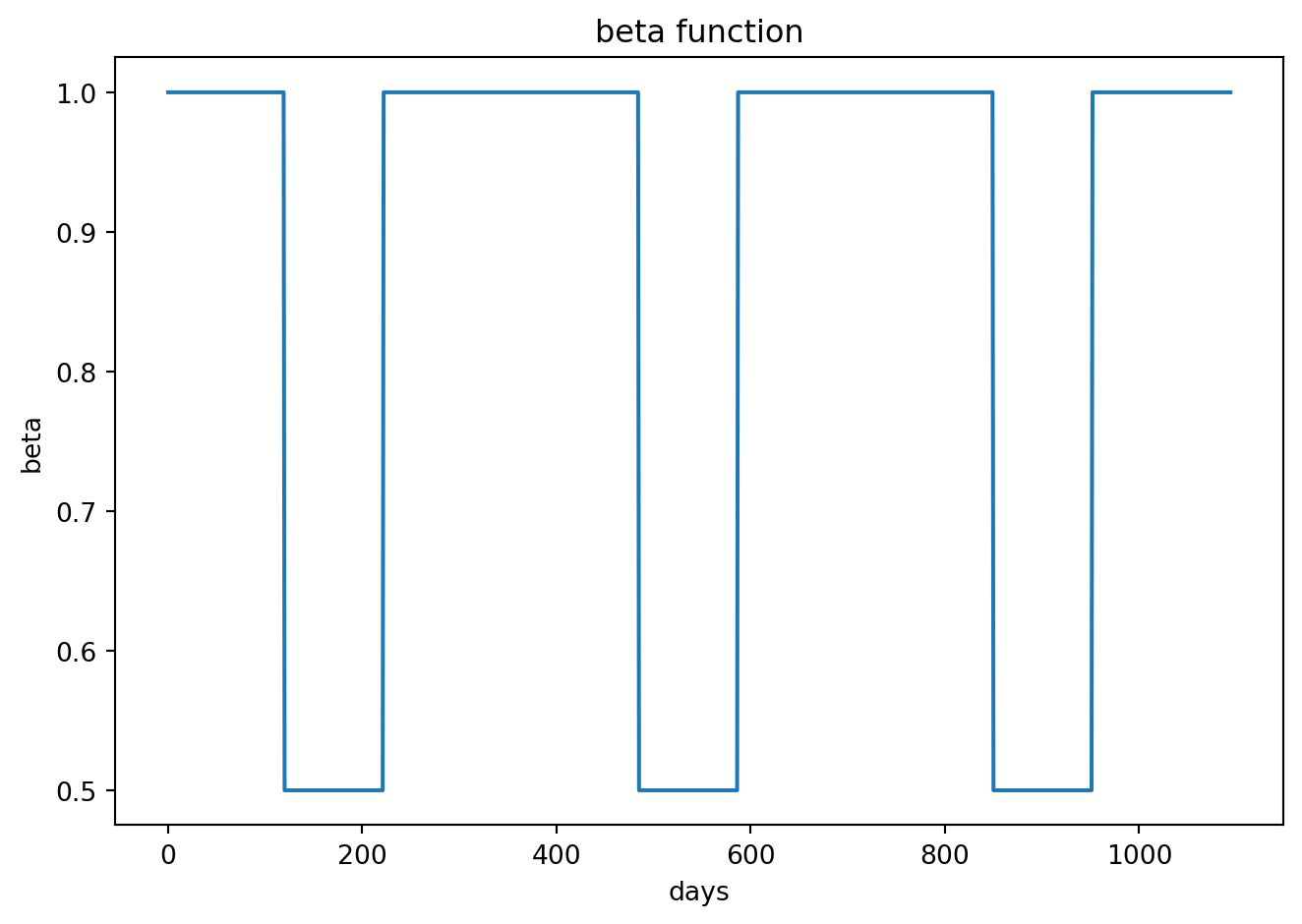
sim = BasicSimulator(rume)
with sim_messaging(live = False):
out = sim.run(
rng_factory=default_rng(5),
)
out.plot.line(
geo=out.rume.scope.select.all(),
time=out.rume.time_frame.select.all(),
quantity=out.rume.ipm.select.compartments("I"),
title="Infectious dynamics with seasonal forcing",
)Loading gpm:all::init::population (epymorph.adrio.acs5.Population):
|####################| 100% (0.691s)
Running simulation (BasicSimulator):
• 2015-01-01 to 2017-12-30 (1095 days)
• 1 geo nodes
|####################| 100%
Runtime: 0.218s